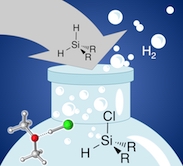
Lewis-Base Catalyzed Selective Chlorination of Monosilanes
HCl/ether at work: A preparatively facile, highly selective synthesis of bifunctional monosilanes R2SiHCl, RSiHCl2and RSiH2Cl is reported. By chlorination of R2SiH2 and RSiH3 with concentrated HCl/ether solutions the stepwise introduction of Si-Cl bonds is readily controlled by temperature and reaction time for a broad range of substrates. In a combined experimental and computational study, we establish a new mode of Si-H bond activation assisted by Lewis bases such as ethers, amines, phosphines, and chloride ions. Elucidation of the underlying reaction mechanisms shows that alcohol assistance through hydrogen-bond networks is equally efficient and selective. Remarkably, formation of alkoxysilanes or siloxanes is not observed under moderate reaction conditions.
Chem. Eur. J. 24, 17796–17801 (2018)
in cooperation with Prof. Auner (Frankfurt)
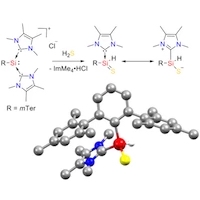
S–H Bond Activation in Hydrogen Sulfide by NHC-Stabilized Silyliumylidene Ions
Reactivity studies of silyliumylidenes remain scarce with only a handful of publications to date. Herein we report the activation of S–H bonds in hydrogen sulfide by mTer-silyliumylidene ion A (mTer = 2,6-Mes2-C6H3, Mes = 2,4,6-Me3-C6H2) to yield an NHC-stabilized thiosilaaldehyde B. The results of NBO and QTAIM analyses suggest a zwitterionic formulation of the product B as the most appropriate. Detailed mechanistic investigations are performed at the M06-L/6-311+G(d,p)(SMD: acetonitrile/benzene)//M06-L/6-311+G(d,p) level of density functional theory. Several pathways for the formation of thiosilaaldehyde B are examined. The energetically preferred route commences with a stepwise addition of H2S to the nucleophilic silicon center. Subsequent NHC dissociation and proton abstraction yields the thiosilaaldehyde in a strongly exergonic reaction. Intermediacy of a chlorosilylene or a thiosilylene is kinetically precluded. With an overall activation barrier of 15 kcal/mol, the resulting mechanistic picture is fully in line with the experimental observation of an instantaneous reaction at sub-zero temperatures.
in cooperation with Prof. Inoue (München)
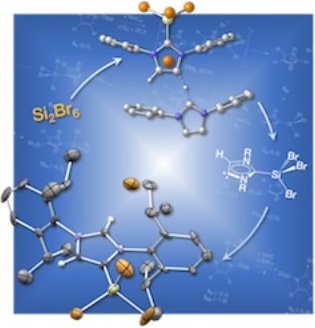
Reactions of Si2Br6 with N‐Heterocyclic Carbenes
A combined experimental and theoretical study on the reaction of Si2Br6 with N‐heterocyclic carbenes is reported. Employment of an imidazole‐2‐ylidene with methyl groups in C4‐ and C5‐position results in the disproportionation of Si2Br6 into the adducts NHC→SiBr2 and NHC→SiBr4. According to expectation, the hydrogenated derivative 1,3‐bis(2,6‐diisopropylphenyl)imidazol‐2‐ylidene forms analogous disproportionation products of Si2Br6 at low temperatures, whereas reaction at higher temperatures furnishes the 4‐SiBr3‐substituted NHC. The underlying formation mechanism explored by means of density functional theory calculations features an abnormal carbene intermediate.
Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 17, 982–988 (2018)
in cooperation with Prof. Auner (Frankfurt)
Thermal Synthesis of Perchlorinated Oligosilanes: A Fresh Look at an Old Reaction
Old reaction, new tricks: A complex mixture of small oligosilanes is produced by quenching the thermal reaction of SiCl4 and elemental silicon. A combined theoretical and experimental reinvestigation of the long-known (SiCl2)xsynthesis sheds new light on the reaction product and its reactivity. The Supporting Information provides, among other things, a comprehensive compilation of computed 29Si NMR chemical shifts for cyclic and acyclic perchlorosilanes, most of which have not been studied experimentally yet.
Chem. Eur. J. 23, 12399–12405 (2017)
in cooperation with Prof. Auner (Frankfurt)
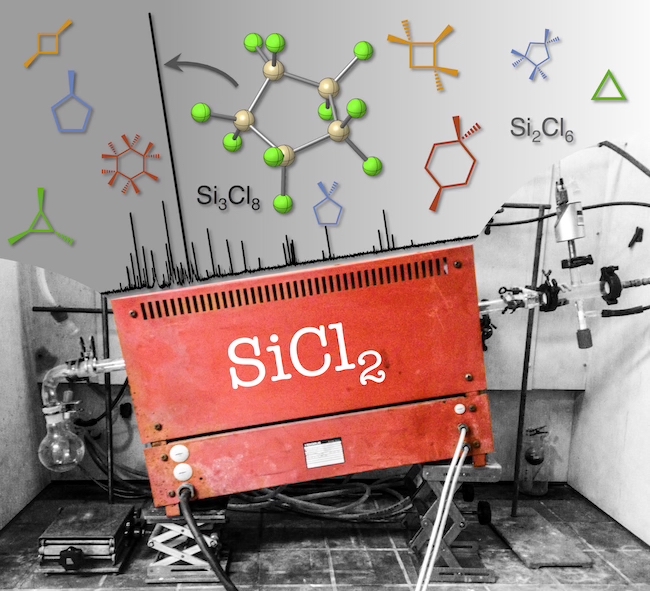
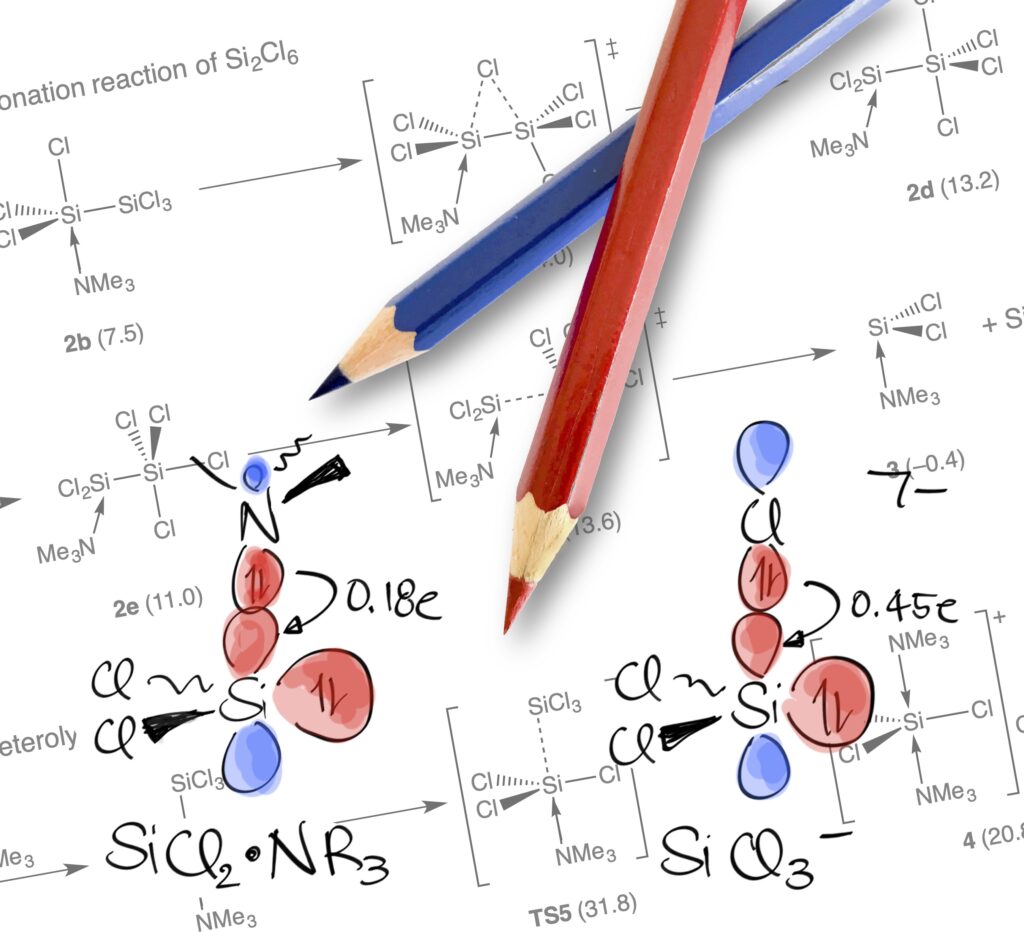
Unraveling the Amine-Induced Disproportionation Reaction of Perchlorinated Silanes—A DFT Study
A neo twist: A DFT study on the amine-induced disproportionation reaction of Si2Cl6 to neo-Si5Cl12 discloses a stepwise rather than a concerted silylene insertion mechanism, which was generally accepted for over half a century. The resulting picture appears generalizable to the related chloride-induced chemistry recently explored.
Chem. Eur. J. 22, 14328–14335 (2016); Chosen as “Hot Paper”
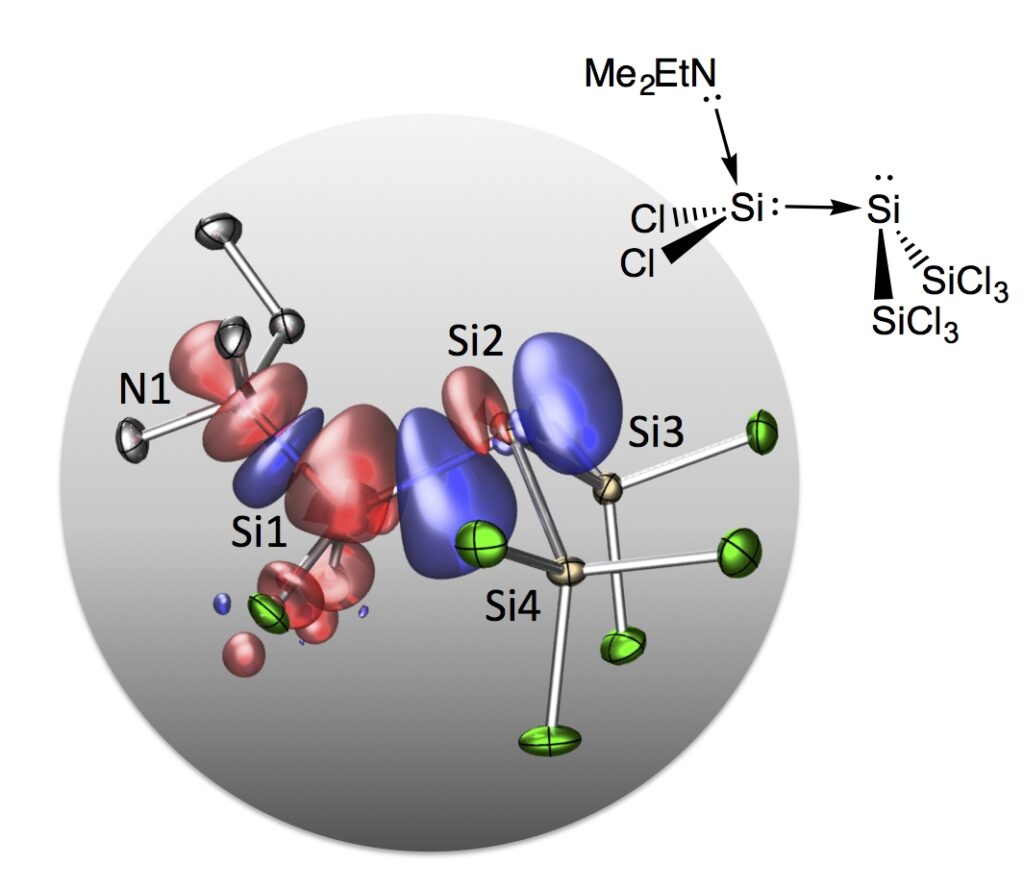
A Disilene Base Adduct with a Dative Si–Si Single Bond
Give and take: A perchlorodisilene amine adduct with an unusually bent structure was isolated by freeze-quench crystallization. The quantum-chemical bond analysis discloses dative N1⟶Si1 and Si1⟶Si2 bonds leading to a push–pull stabilization of the central SiCl2 group.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55,1782–1786 (2016)
in cooperation with Prof. Schneider (Göttingen), Dr. Linser (MPI Göttingen), and Prof. Auner (Frankfurt)
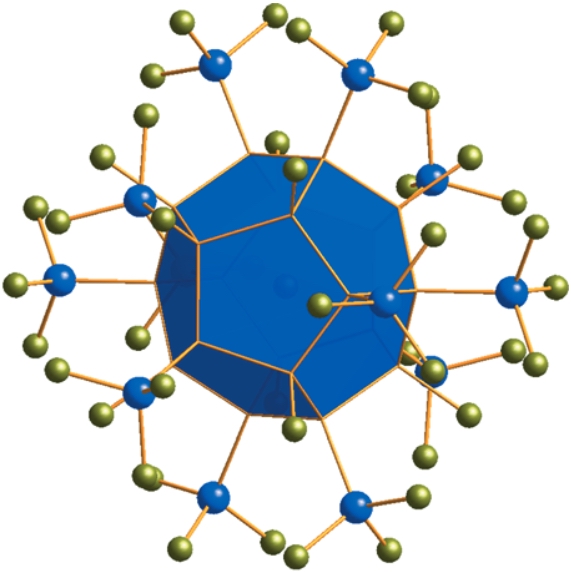
One-Step Synthesis of a [20]Silafullerane with an Endohedral Chloride Ion
As simple as this: A stable, crystalline [20]-silafullerane forms in preparatively useful yields through wet-chemical self-assembly from Si2Cl6 and chloride ions in the presence of an amine. Each silicon dodecahedron contains an endohedral chloride ion that imparts a net negative charge. Eight chloro substituents and twelve trichlorosilyl groups are attached to the surface of each cluster in a strictly regioregular arrangement.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 5429–5433 (2015); Highlighted as “Very Important Paper”
in cooperation with Prof. Wagner (Frankfurt)
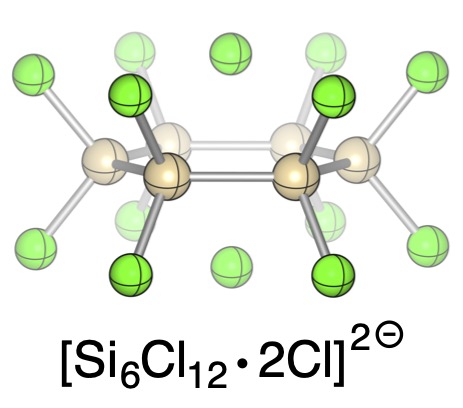
Chloride-induced aufbau of perchlorinated cyclohexasilanes from Si2Cl6 – A mechanistic scenario
As simple as this: Chloride addition to Si2Cl6 provides efficient synthetic access to perchlorocyclohexasilane dichloride adducts. The reaction mechanism has been elucidated in a combined theoretical and experimental study: chloride-induced SiCl3− liberation from Si2Cl6 triggers the formation of higher silanide anions, which dimerize in a head-to-tail fashion to the cyclic final products.
Chem. Eur. J. 20, 9234–9239 (2014); Conference Issue: 17th ISOS, Berlin
in cooperation with Prof. Wagner (Frankfurt)
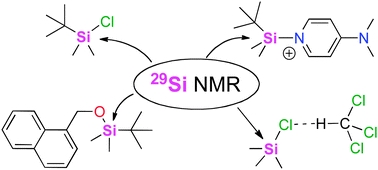
The calculation of 29Si NMR chemical shifts of tetracoordinated silicon compounds in the gas phase and in solution
Aiming at the identification of an efficient computational protocol for the accurate NMR assessment of organosilanes in low-polarity organic solvents, 29Si NMR chemical shifts of a selected set of such species relevant in organic synthesis have been calculated relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS, 1) using selected density functional and perturbation theory methods. Satisfactory results are obtained when using triple zeta quality basis sets such as IGLO-III. Solvent effects impact the calculated results through both, changes in substrate geometry as well as changes in the actual shieldings. Spin–orbit (SO) corrections are required for systems carrying more than one chlorine atom directly bonded to silicon. Best overall results are obtained using gas phase geometries optimized at MPW1K/6-31+G(d) level in combination with shielding calculations performed at MPW1K/IGLO-III level in the presence of the PCM continuum solvation model.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 16642–16650 (2014)
in cooperation with Prof. Zipse (München)